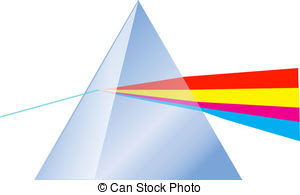
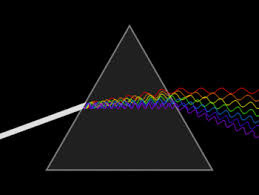
Dual nature of Light
(a) Particle (b) Wave
Light has dual nature particle (photon) as well as wave.
What is Photon. Photon is define as, very very tiny (smallest) particle/packet of energy. The rest mass of photon is zero.
What is wave. Wave is define as, A wave can be described as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location.
Albert Einstein's photoelectric effect experiment proves that light can behave as a particle while
Thomas Young's double-slit experiment shows that it also behaves as a wave.
Albert Einstein proved that in 1905, light could behave as a particle by showing that a beam of light could eject electrons from metal when a suitable radiation (invisible ray) fall on metal, This suggested that light consisted of photons that could eject electrons of similar frequency. Einstein's discovery altered the prevalent theory at the time, which held that light was only a wave.
And light has the wave nature also, it has proved earlier by Young in 1801. In his experiment, Young shone light between two parallel slits, causing the light waves to interfere with each other and form a patter of dark and light bands. If light was primarily a particle, it would have formed two parallel lines.
Quantum mechanics explains the duality of light by describing it as a wave-packet. A wave-packet refers to waves that may interact either as spatially localized, acting as particle, or interacting like waves. This means light photons can either act as a particle or wave, depending on the circumstances.

Making wave by rope


Making wave by water


Wave example


Electromagnetic wave


Electromagnetic wave

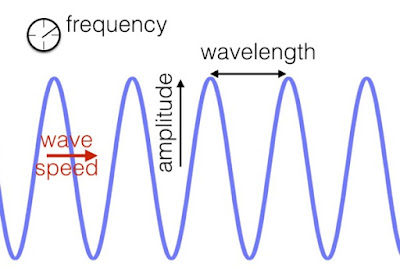
Wave details


Wave example


Electromagnetic wave


Electromagnetic wave