The Solar Hero. (The Sun)
What is the Sun....?
Actually The Sun is just a star of about billions stars in our galaxy, at the center of the solar family (Solar system).
Sun is the main part of solar family and most important needs for our planet (The Earth). Because the main source of energy for this earth is the Sun.
Sun is the central part of our solar family (Solar system), it lies in orian arm of milky way galaxy.
There are nine major planets around the Sun in their respective orbits, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto (no longer an official planet).
Every planets, sub planets revolve around the sun in their respective elliptical orbit in a fix rate. The nearest planet from the sun is Mercury, and the fares planet is Neptune. And the positions of our earth from the sun is third. the nearest star of sun is proxima century.
Sun consumes approx 4.0 million tons hydrogen per second, In which compositions created by sun are, 75% hydrogen, 23% helium, and 2% heavier elements.
Sun is the largest object in solar family, and it contain 99.86% of total mass of solar system. And rest contain by Jupiter.
The age of sun is approx 4.6 billion years old, and probably that it will be continue exist more 5 billion years from present be converting of hydrogen in to helium.
The sun's light reach on the earth in (there are some opinions on the basis of researchers) a. 8min 20sec, b. 8min 17 sec, c. 8min 9sec. c is the recently research result.
The sun diameter is 1,390,000 km, And Its core temperature is 15 million ºC. and the mass of sun is 1.989e30kg.
In which surface temperature is 5,500 ºC. Cooler (3,800 ºC) surface areas are called sun spots.
The sun radiates heat and a steady stream of charged particles known as the solar wind, which blows about 280 miles (450 kilometers) per second throughout the solar system.
Solar flares are jets of particles that burst from the sun and can disrupt satellite communications and knock out electricity on Earth.
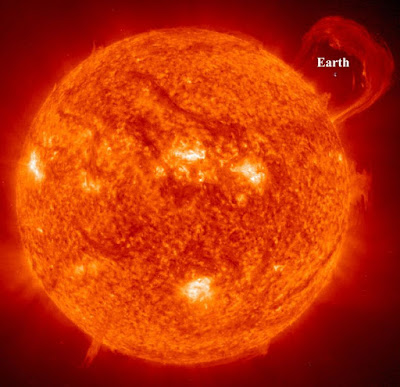 |
| Earth in compare of sun. |
 |
| Solar family in row. |
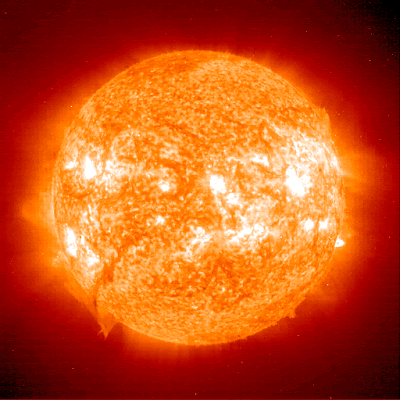 |
| The sun. |
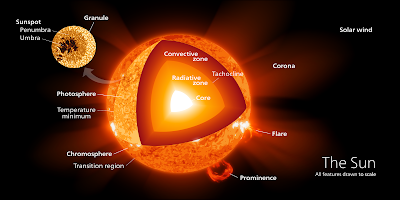 |
| Inside layer of the Sun. |